For a grade 3 meningioma you might have an MRI scan. For a grade 1 meningioma you might have an MRI scan every year for up to 5 years.
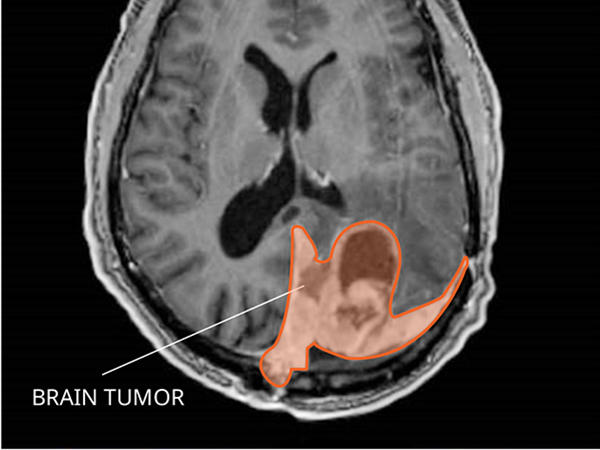 Meningioma Diagnosis And Treatment National Cancer Institute
Meningioma Diagnosis And Treatment National Cancer Institute
But they can also grow on parts of the spinal cord.

Treatment for meningioma brain tumor. Stereotactic radiosurgery SRS is a type of radiation treatment that aims several beams of powerful radiation at a precise point. As many as 90 are benign not cancerous. About 40-60 of benign tumors are meningiomas.
The major goal of radiation treatment is to kill meningioma tumor cells while minimizing damage to surrounding normal brain tissue. However natural treatment options treat any meningioma effectively. Typical treatment of a meningioma is dependent on the location and severity of the tumor itself.
There are three treatment options for meningiomas. Often meningiomas cause no symptoms and require no immediate. The Brain Tumor Center and the Skull Base Surgery Program provide leading treatment options for patients with meningiomas.
Moreover some meningiomas are also qualified as atypical which means that they are neither malignant nor benign but something in between the two. The first treatment for a malignant meningioma is surgery if possible. Our neurosurgeons have particular expertise in removing and treating meningiomas including in areas of the skull base that traditionally are difficult to reach.
Most meningiomas occur in the brain. Meningiomas are normally treated according to their grade but their location size and the symptoms youre having will also affect which treatment youre offered. Contrary to its name radiosurgery doesnt involve scalpels or incisions.
The Meningioma is a primary intracranial tumor that is one of the most common benign tumors within the cranium head. You then have an MRI scan every 2 years. About 15 of all primary intracranial tumors both benign and malignant are meningiomas.
For a grade 2 meningioma you might have an MRI scan every 6 to 12 months. Since the vast majority of meningiomas are benign noncancerous they are most commonly treated with surgery. There are also clinical trials underway to identify new therapies.
Often meningiomas cause no symptoms and require no immediate. Radiation therapy uses high-energy X-rays to kill cancer cells and abnormal brain cells and to shrink tumors. Meningiomas are tumors which arise from meninges which are the membrane surrounding the brain spinal cord.
People who are diagnosed with a grade 1 meningioma are often put on active monitoring treatment with surgery and radiotherapy offered at a later date if needed. Observation surgery and radiation. A meningioma is a tumor that arises from a layer of tissue the meninges that covers the brain and spine.
Radiation therapy that involves radiation to the head may increase the risk of a meningioma. Radiosurgery typically is done in an outpatient setting in a few hours. The treatment for grade 2 and 3 meningiomas is usually surgery where possible followed by radiotherapy.
Sometimes radiation can help reduce the size of a meningioma. The goal of surgery is to obtain tissue to determine the tumor type and to remove as much tumor as possible without causing more symptoms for the person. But they can also grow on parts of the spinal cord.
Total removal of a meningioma is preferred since it lessens the chances of the tumor returning. However most meningiomas that occur are benign noncancerous but rarely some meningiomas may also be malignant cancerous. Radiation therapy for meningiomas involves externally beaming from a machine high energy X-rays at the tumor site known as external beam radiation.
Surgery is the most common treatment for a meningioma. Elements of holistic treatment include improving circulation with coconut oil and other natural remedies making dietary changes for health and getting plenty of carotenoids. Radiation therapy options for meningiomas include.
Most meningiomas occur in the brain. For some total resection surgery is all that is needed for treatment followed by periodic imaging to monitor any recurrence of a tumor. Meningiomas grow on the surface of the brain or spinal cord and therefore push the brain away rather than growing from within it.
After 5 years you have an MRI scan every 2 years. Most are considered benign because they are slow-growing with low potential to spread. Most people with atypical and anaplastic meningiomas receive further treatments.
Radiation therapy may be an option if the tumor cannot be treated effectively through surgery. If a meningioma is benign and in a part of the brain where neurosurgeons can safely completely remove it surgery is likely to be the only treatment needed. As many as 90 are benign not cancerous.
Small-cell lung cancer spreads quickly. Even if the cancer hasnt spread to your brain your doctor may recommend radiation to the brain prophylactic cranial irradiation.
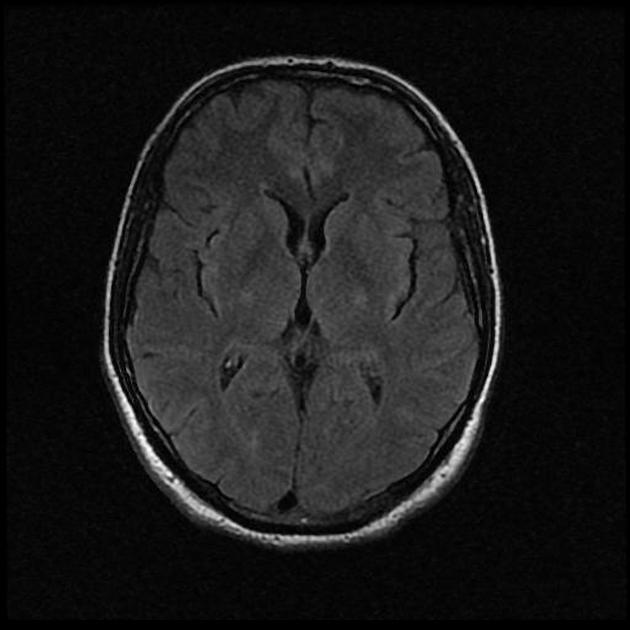 Brain Metastasis Small Cell Lung Cancer Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
Brain Metastasis Small Cell Lung Cancer Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
SCLC can spread to the brain rapidly often before a first cancer diagnosis is even made.

Small cell lung cancer spread to brain. Roughly 10 percent of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer NSCLC have brain metastases at their initial diagnosis. Small cell lung cancer frequently spreads to the brain even if there are no spots seen on CT scan or MRI of the brain. It can metastasize to the brain.
Lung cancer is the most common cancer that spreads to the brain. Bone pain like pain in the back or hips Nervous system changes such as headache weakness or numbness of an arm or leg dizziness balance problems or seizures from cancer spreading to the brain. Thats done because the cancer cells that are present in the brain are often too small to be detected by the scans.
Due to the fact that there is little variation in prostate specific antigen levels this form of cancer is normally diagnosed at an advanced stage after metastasis. As many as 40 percent will eventually develop brain tumors at some stage. Symptoms of small cell lung cancer can include.
Small-cell carcinoma of the prostate In the prostate small-cell carcinoma SCCP is a rare form of cancer approx 1 of PC. Typically it will cause some of the following symptoms. PCI is generally given to individuals who have a good response to initial therapy and are healthy enough to undergo the treatment.
When Surgery Isnt an Option If your non-small-cell lung cancer NSCLC has spread to the brain your doctor has to take extra care to get your treatment just right. The symptoms of brain metastasis can vary. Metastasis or cancer spread is a top concern for people who have small cell lung cancer.
Lung cancer spread to brain how long to live - Lung cancer is known to spread to the brain about 40 percent of cases where metastasis has occurred. 9 Both non-small cell lung cancer and small cell lung cancer can be involved. Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer deaths in both women and men in the United States Canada and China.
Metastasis is the medical term used to describe cancer that has spread beyond the initial tumor to other organs of the system. For small cell lung cancer doctors sometimes use radiotherapy to the brain to kill any cancer cells that might have spread into the brain but are too small to see. Once small cell brain cancer is present the cancer has already metastasized from the lungs to the brain.
Once the cancer has metastasized to the brain the symptoms can include. Without treatment the average life expectancy for a person with an extensive-stage small cell lung cancer diagnosis is two to four months. Approximately 10 of patients present with brain metastases at the time of initial diagnosis and an additional 40 to 50 will develop brain metastases some time during the course of their disease.
Facts You Should Know About Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Small cell lung cancer can grow quickly and affect the brain bones and liver and adrenal glands. About 20 to 40 percent of adults with non-small cell lung cancer go on to develop brain metastases at some point during their illness.
Extensive stage small cell lung cancer SCLC is in the stage where it has spread to other parts of the body such as the other lung or the brain. Radiotherapy to the brain Radiotherapy uses high energy x-rays to treat cancer cells. The most frequent metastatic sites are.
Lung cancer can affect any part of the lung. As many as 40 of people diagnosed with lung cancer will develop brain metastases at some point. But in general it seems that small cell type is likely to spread to the brain than non-small cell type.
Your brain controls everything. For instance cancer cells in the lung can travel to the bone and grow there. Because SCLC is an aggressive cancer and can spread to the brain PCI is used to destroy any microscopic cancer cells that may have reached the brain.
This can prevent the cancer from spreading there. With lung cancer is considered to be the fourth stage of the disease. Cancer cells can spread to other parts of the body.
Diagnosing Small Cell Cancer. You usually have 5 to 10 treatments over one week. When cells of the lung start to undergo a degenerative transformation in appearance and start growing rapidly in an uncontrolled manner the condition is called lung cancer.
Small-cell lung cancer responds well to chemotherapy using medications to kill cancer cells and radiation therapy using high-dose X-rays or other high. Some doctors will advise radiation to the brain to wipe out microscopic cancer cells. Small cell lung cancer that spreads is treatable but generally isnt curable.
The prognosis of patients with brain metastases from SCLC is poor despite years of research. Cancer that starts in the lung is called lung cancer. When cancer cells spread its called metastasis.
At the metastasis stage both small cell and non-small cell lung cancer can affect the brain. When small cell lung cancer spreads to distant organs extensive-stage SCLC it can cause other symptoms which may include.